History of the Turks and Caicos Sea Salt Industry
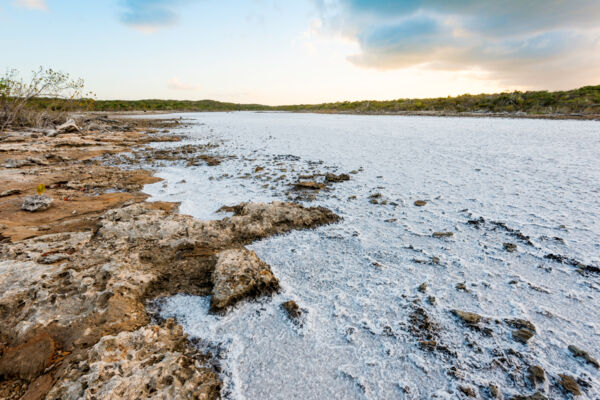

The Turks and Caicos consists of many small low-lying islands, and every larger island in the archipelago has at least one natural saltwater pond or lagoon. These ponds often have some connection to the ocean. In some cases this is by natural inlets or channels, others are replenished by abnormally high tides or subterranean cave systems. As the trapped ocean water in these ponds evaporates in the typically hot Turks and Caicos climate, salt crystals naturally collect in places.
Salt exports from the Turks and Caicos began before recorded history. It’s known that the indigenous Taino pre-Columbian inhabitants would gather some of this naturally occurring salt and trade it with the inhabitants of Hispaniola for honey and fruit, and evidence also suggests that they may have also exported salted bonefish! Later on, early European explorers would also stop by to collect salt.

The Turks and Caicos has many high salinity ponds, which can be found on nearly every major island in the archipelago. However, not many of the ponds naturally produce large amounts of salt, as water inflow must be in balance with evaporation rates. A notable productive natural salt pond is the Proggin Bay flat, which is in the Frenchman's Creek and Pigeon Pond Nature Reserve on Providenciales.
Evidence suggests that the natural salt ponds were quite valuable to the pre-Columbian Lucayan peoples that previously inhabited the Turks and Caicos, as major settlement sites have been located near such sites.
In previous centuries, salt was a very valuable commodity necessary for food preservation. In the late 1600s, British colonists in Bermuda recognized the potential of the Turks and Caicos marine ponds for salt raking, and by the end of the century, they had begun to develop the natural ponds into salinas to increase output.
Salt Industry Development in the Islands
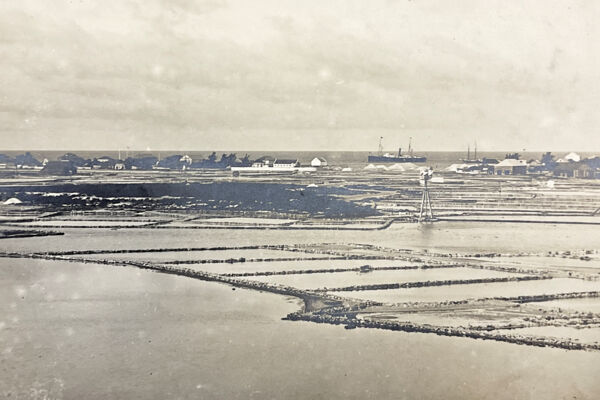
Over the next two hundred years, extensive salt works were built on Grand Turk, Salt Cay, and South Caicos, along with the infrastructure needed to support the industry and populations.
By this time, Grand Turk, South Caicos, and Salt Cay each had more or less every available pond developed, and expansion to West Caicos and possibly a pond on the southwest of Providenciales was being considered. However, it was not to happen.
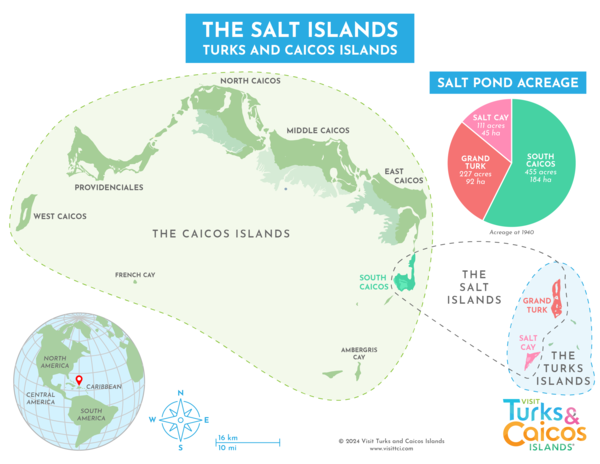
Salinas by Island
Export Values and Quantities
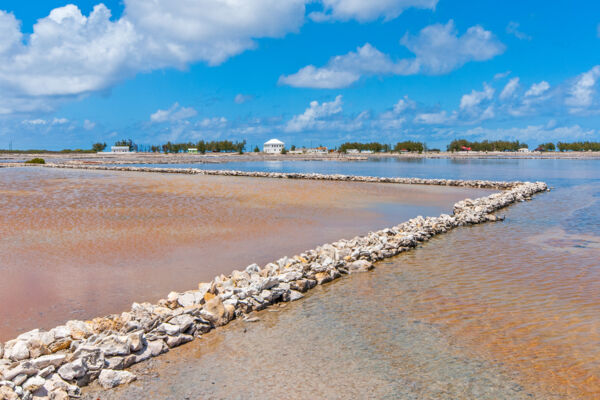

Production of salt peaked at the end of the 1800s and the start of the 1900s. 1897 was the record year, with a total of 2,236,008 bushels of salt produced (about 173 million pounds, or 78 million kilograms). A bushel of coarse salt, the typical variety produced in the islands, weighed 75-80 pounds (35-36 kg).
During the salt industry days, about 800 acres (324 hectares) of salina were being utilized across the three islands and over 80 miles (129 km) of dividing walls stood.
The price of salt varied considerably, ranging from an annual export value of approximately £34,000 in 1897 (around $4.8 million in 2023 US dollars) to £12,000 in 1934 (around $1 million in 2023 US dollars). The average annual export value between 1897 and 1934 was £23,000.
Salt Exports by Year (Bushels)
| Annual Salt Exports from Turks and Caicos | ||
| Year | Bushels Exported | Price (Cents/Bushel) |
| 1887-1891 | 1,618,451 average | 8.24 |
| 1892-1896 | 1,750,207 average | 7.6 |
| 1897-1901 | 1,804,372 average | 7.44 |
| 1902 | 1,656,750 | 7.44 |
| 1903 | 1,806,694 | 6.28 |
| 1904 | 1,005,248 | 7.14 |
| 1905 | 961,299 | 7.32 |
| 1906 | 1,043,474 | 6.56 |
| 1907 | 1,420,052 | 5.58 |
| 1908 | 1,749,526 | 5.2 |
| 1909 | 1,243,144 | 6 |
| 1910 | 1,143,909 | 6 |
| 1911 | 1,497,207 | 6 |
| 1912 | 1,426,146 | 6 |
| 1913 | 1,782,766 | 5.75 |
| 1914 | 1,683,214 | 5.75 |
| 1915 | 1,745,350 | 5.75 |
| 1916 | 1,534,954 | (no data) |
| 1917 | 1,752,388 | (no data) |
| 1918 | 860,369 | (no data) |
| 1919 | 1,119,274 | (no data) |
| 1920 | 1,905,142 | (no data) |
| 1921 | 1,237,488 | (no data) |
| 1922 | 1,838,188 | (no data) |
| 1923 | 1,627,032 | (no data) |
| 1924 | 1,465,164 | (no data) |
| 1925 | 1,748,105 | (no data) |
| 1926 | 1,510,817 | (no data) |
| 1927 | 781,831 | (no data) |
| 1928 | 1,401,121 | 7.1 |
| 1929 | 1,712,270 | 8.27 |
| 1930 | 1,163,152 | 8.19 |
| 1931 | 754,019 | 6.71 |
| 1932 | 577,494 | 6.93 |
| 1933 | 687,841 | 7.4 |
| 1934 | 522,563 | 7.85 |
| 1935 | 793,747 | 5.62 |
The End of the Industry
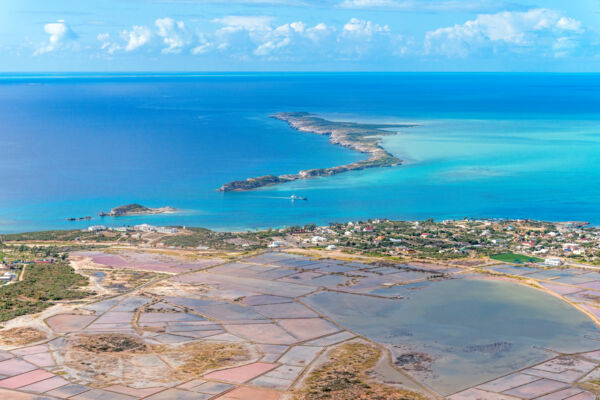

What ultimately doomed the salt industry in the country was the small-scale of production. The islands in the Turks and Caicos are small, with a limited number of ponds that could be developed. Necessary infrastructure such as deep water docks simply cost too much to build and maintain compared to the expected returns. Other sites such as Lake Windsor on the nearby Bahamian island of Great Inagua, proved to be far more financially viable for salt production due to its much greater size. Morton Salt currently produces over a million tons of sea salt per year at this location.
Attempts were made in the mid-1900s to revive dying exports, yet these failed to be remotely profitable.
Today, the only salt produced in the Turks and Caicos is for boutique purposes, and in very limited quantities. Some is gathered on coastlines or on one of the few natural salt flats found in the country, and the remainder is collected from small scale salinas.
The Process
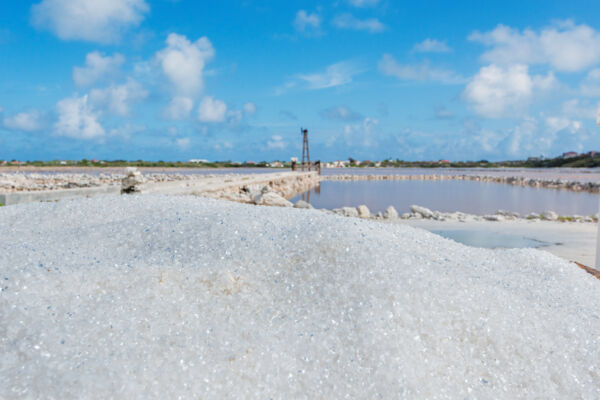

Initial gathering of salt by the Tainos and early European visitors was simply scraping up what accumulated naturally, but by the time the salt industry was in full swing the process was far more advanced.
The natural ocean water ponds on the islands would be split up into different stages of ponds. The largest was typically the pond with the closest connection to the ocean water inlet, and consequently had the highest water content. Sluice gates separated the ponds and could be opened or closed to allow brine movement between ponds.
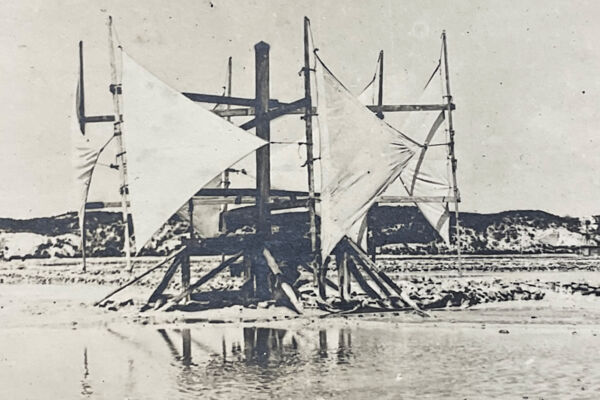
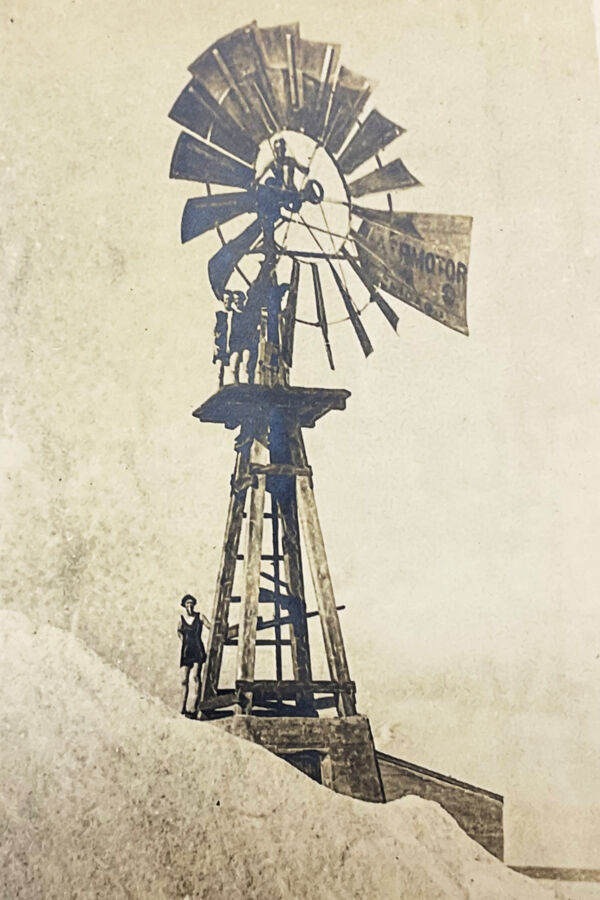
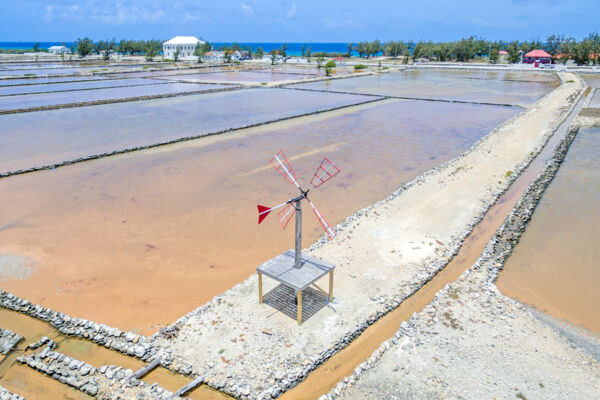
As the water evaporated and the salinity increased, the brine would be moved by a windmill or human-powered pump to progressively smaller and higher salt content ponds until it crystallized. This system allowed for smaller final stages of ponds that were easier to keep free of unwanted water seepage, a consistent supply of salt, and also provided a bit of protection against major loss caused by wall failure.

The salt crystals would be raked by hand into small piles, shoveled into baskets, wheelbarrows, or donkey carts, and moved to a central location. Here it would sit until a ship arrived. The salt would then be shoveled into bags to make up forty-pound (18 kg) sacks. Due to the total lack of deep-water ports in the country, the sacks would be ferried by small boats (called lighters) out to the waiting ship, where the salt would be deposited into the hold.
The work of gathering salt was a nasty and difficult job. Constant contact with the brine caused skin problems and the intense sun reflected by the brilliant white salt crystals would bring on premature vision issues and blindness.
Turks and Caicos salt was considered to be of the highest quality. During the American Revolutionary War, George Washington personally requested salt from the Turks Islands.
What Can Be Seen Today
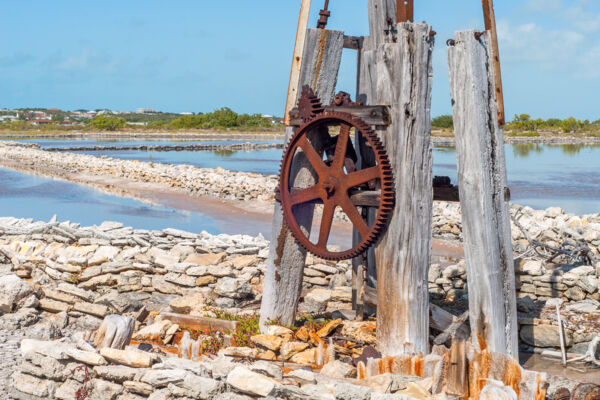

Much still remains of the salt industry on Grand Turk, South Caicos, and Salt Cay. The majority of these ruins are the low simple walls that divide up the salinas, yet complex gate and sluice arrangements can also be seen. Some notable features still standing are the Boiling Hole on South Caicos, and the White House and Deane's Dock inlet sluice gates on Salt Cay. As both islands have seen very little development since the salt days, visiting Salt Cay and South Caicos is like stepping back in time.
A fascinating glimpse into salt days is also the 1941 Hollywood feature film Bahama Passage. Most of this film was shot on Salt Cay when salt production was still active.








